Schottky diodes and Zener diodes are both commonly used diodes, but they have significant differences in structure, working principle and application. Here are the main similarities and differences:
Similarities between Schottky and Zener
- Unidirectional conductivity: Both have unidirectional conductivity under normal working conditions.
- Application scenarios: Both can be used for power supply and signal conditioning, but the specific functions and parameters are different.
- Semiconductor devices: Both are electronic devices based on semiconductor materials, which use the characteristics of P-N junction or metal-semiconductor junction to achieve their respective functions.
What are the differences between Zener and Schottky?
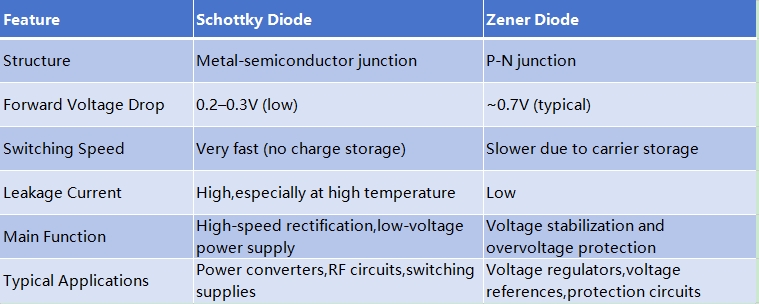
1.Structure
- Schottky diode: uses a metal-semiconductor junction structure (such as metal in contact with N-type semiconductor), and does not use a traditional P-N junction.
- Zener diode: uses a P-N junction structure, which can stabilize the clamping voltage during reverse breakdown through doping process adjustment.
2.On-voltage
- Schottky diode: The forward conduction voltage is low, generally 0.2-0.3V (silicon-based material), which is better than the 0.7V of traditional diodes. This gives it an advantage in high-frequency and low-voltage applications.
- Zener diode: The forward conduction voltage is similar to that of ordinary diodes, generally 0.7V (silicon-based material). When reverse conducting, the voltage is stabilized at the designed Zener voltage.
3.Working principle
- Schottky diode: Relying on the Schottky barrier between metal and semiconductor, electrons quickly pass through the barrier when forward biased, forming a low voltage drop.
- Zener diode: Through the high doping process of the P-N junction, a breakdown effect occurs when the reverse voltage reaches the Zener voltage, and it is stabilized at the Zener voltage.
4.Reverse characteristics
- Schottky diode: The reverse breakdown voltage is low (generally below 50V) and the withstand voltage is weak, so it is usually used in low-voltage applications.
- Zener diode: The reverse breakdown voltage range is wide (such as 2V to hundreds of volts), and it can stably clamp the voltage after reverse breakdown, and is often used in voltage stabilization circuits.
5.Applications
- Schottky diode: It is mainly used in high-frequency rectification, low-voltage drop power supplies, and fast switching circuits.
- Zener diode: It is used in voltage regulators, voltage references, and overvoltage protection, and plays a protective role when the voltage exceeds the Zener voltage.
6.Switching speed
- Schottky diode: The switching speed is extremely fast, because there is no minority carrier storage effect, it is suitable for high-speed circuits.
- Zener diode: The switching speed is not as fast as Schottky diode because the carrier recovery time of the P-N junction is longer.
7.Leakage current
- Schottky diode: The reverse leakage current is large, especially at high temperatures.
- Zener diode: The reverse leakage current is usually small, suitable for stable voltage clamping applications.
In summary, the differences between the two are as follows:
How to choose between Schottky and Zener diodes?
- Choose Schottky diodes when your circuit needs low forward loss, high speed, and efficiency, such as in switching regulators or power rectifiers.
- Choose Zener diodes when you need precise voltage control or protection, such as in voltage reference, clamp, or regulator circuits.
Related Products
About Semiware
Semiware has a comprehensive product lineup of circuit protection device products. The company leverages its technology in the semiconductor field and application background in end products to serve customers in the electronics, automotive and industrial markets. For more information, please visit semiware official website: https://en.semiware.com/
At Semiware,we also offer a wide range of diode series,including TVS,rectifier, Schottky,and Zener diodes for different power and protection applications.
👉 Visit our official website to explore detailed product specifications,datasheets,and bulk purchase options:https://en.semiware.com/


Comments (0)